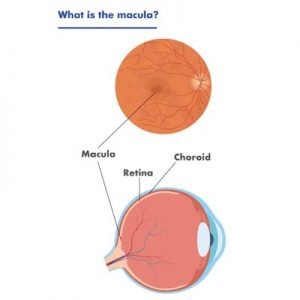
Macular Degeneration
Age-related Macular degeneration (AMD) is a chronic eye disease that affects the central part of the retina, leading to a loss of vision. The disease is often associated with aging and is more common in people over the age of 50. The exact cause of AMD is unknown, but certain factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and family history can increase the risk of developing the disease. Symptoms of AMD include wavy or blurred vision, visual distortion, loss of central vision, change in the perception of color, and trouble recognizing faces.
There are two main types of AMD: dry and wet. Dry AMD develops slowly and causes gradual vision loss, while wet AMD leads to rapid loss of central vision. There is no permanent cure for AMD, but treatments aim at slowing down the progression of the disease and preventing vision loss. Treatments include medication and injections. A healthy and nutritious diet including lots of green leaf vegetables, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy body weight can also help prevent AMD.
Early detection of AMD increases the chance that your optometrists can treat you and can help prevent further loss of vision. Regular eye examinations are crucial to detect AMD early, even if you have no symptoms. We recommend an eye examination every 1-2 years. If it has been a while, consider booking in and our friendly optometrists can check your macular.